Automatic tasks
This sections is in active development, so can be incomplete.
You are progressing in your KuFlow learning!
Now, we want to take you to the next level by addressing processes based on the based-on-Temporal Engine, which are much more powerful although more complex.
Don't worry, we have prepared everything you need so that you can tackle this challenge.
First of all, we need to create a new application, named MyWorker. This will allow us to establish a connection to KuFlow from a third-party app (i.e. our worker).
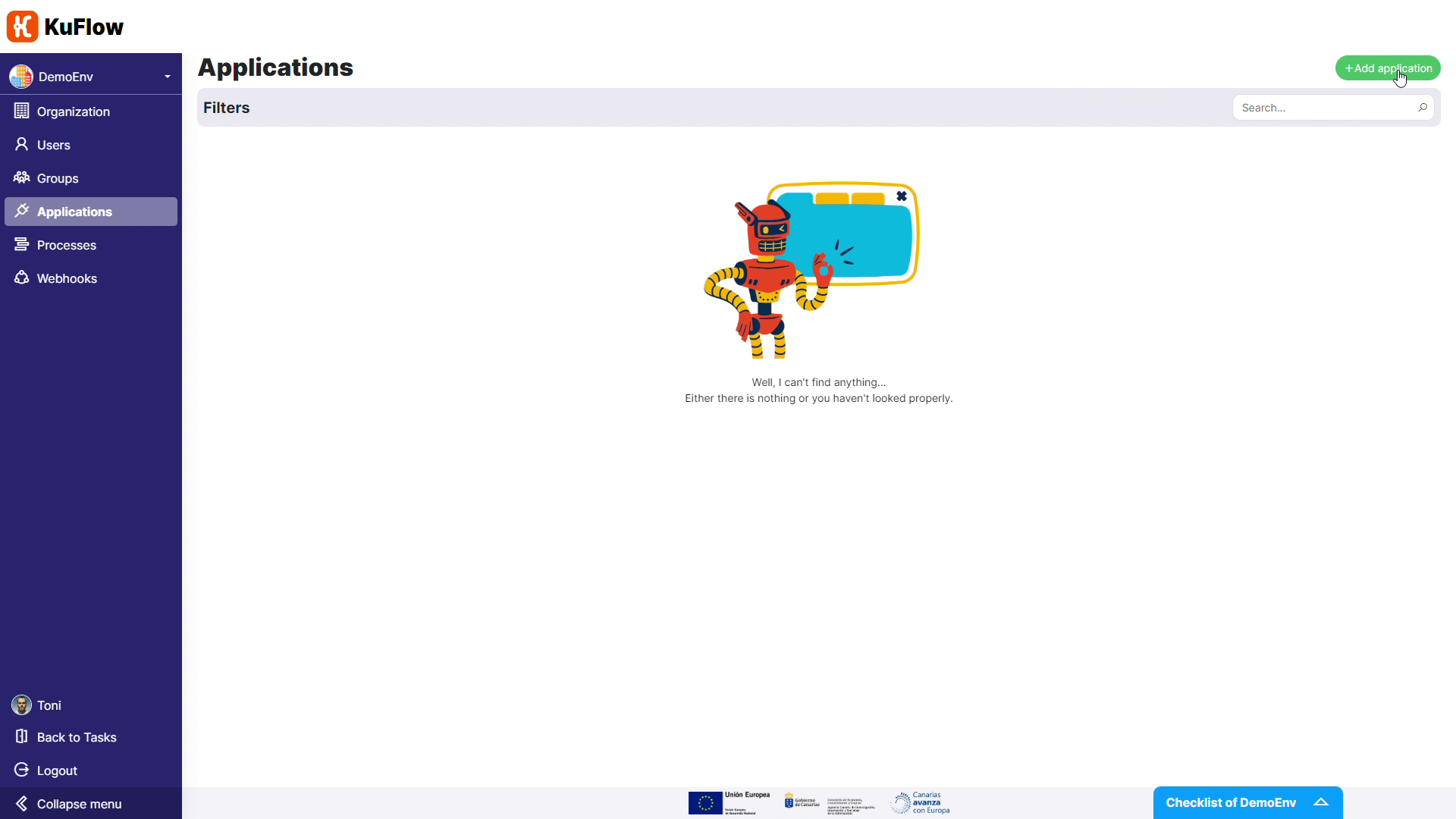
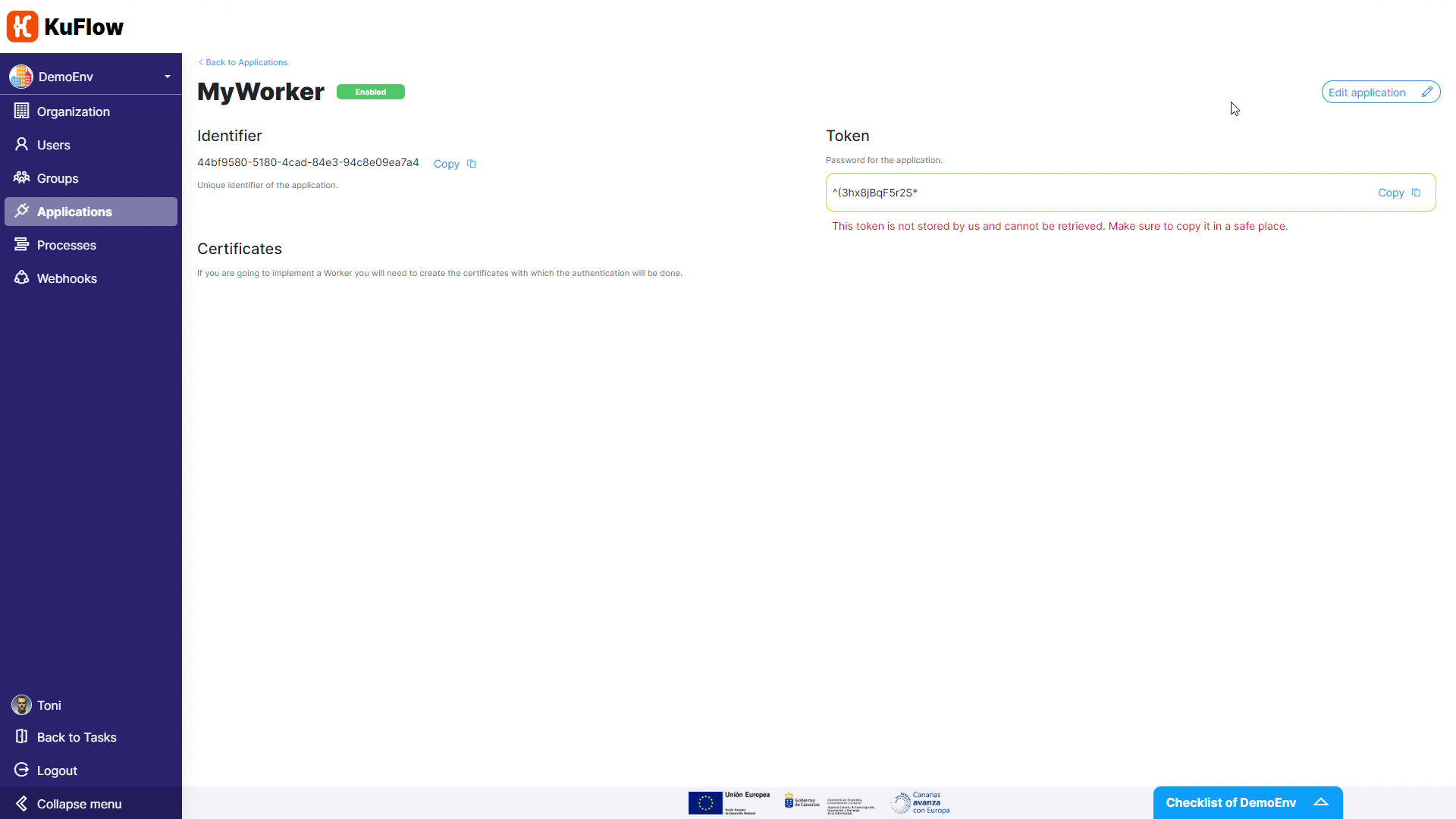
After creating this new application, it will have an Identifier and a Token. Keep this token information in a safe place, since it cannot be retrieved afterwards.
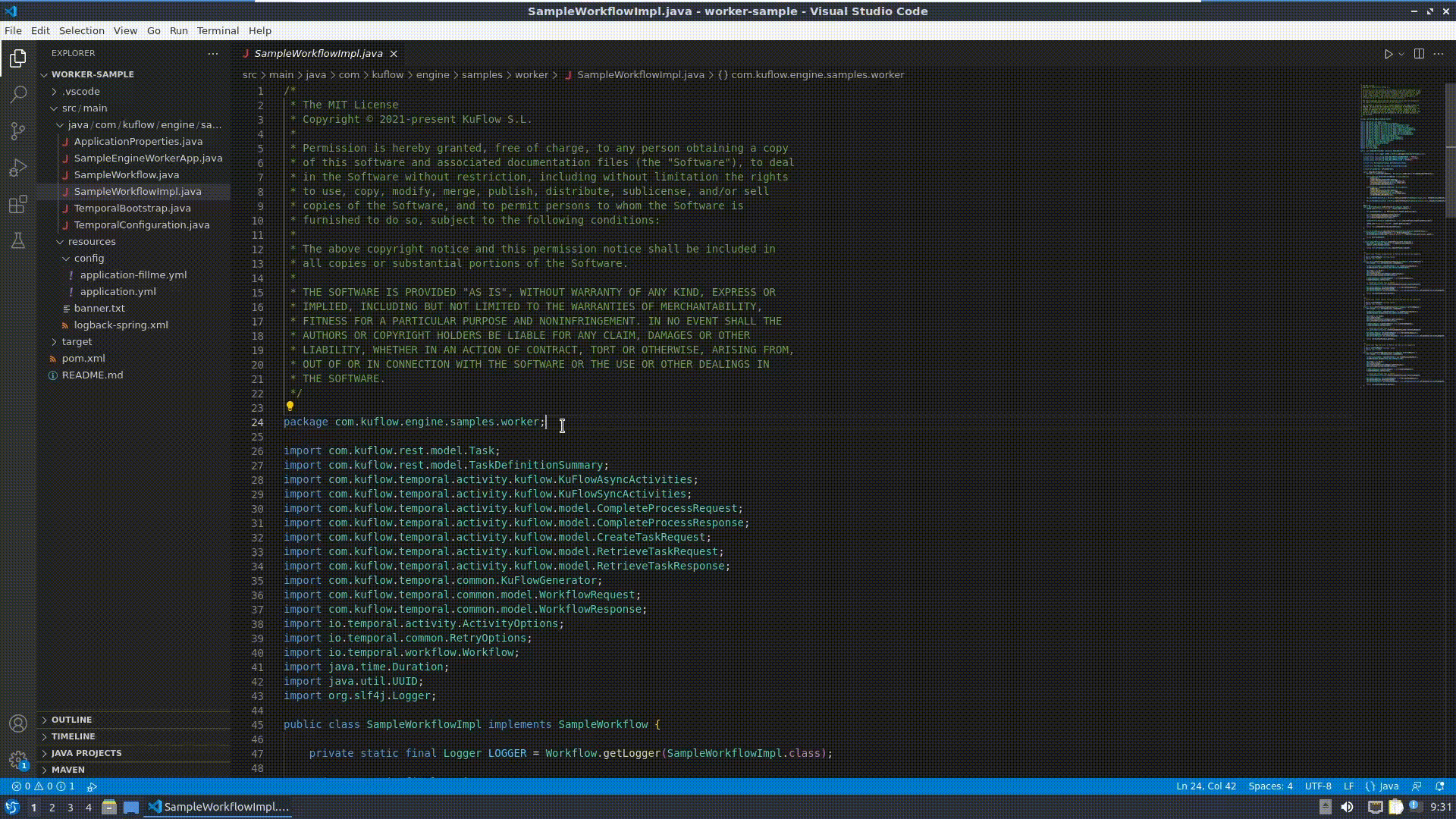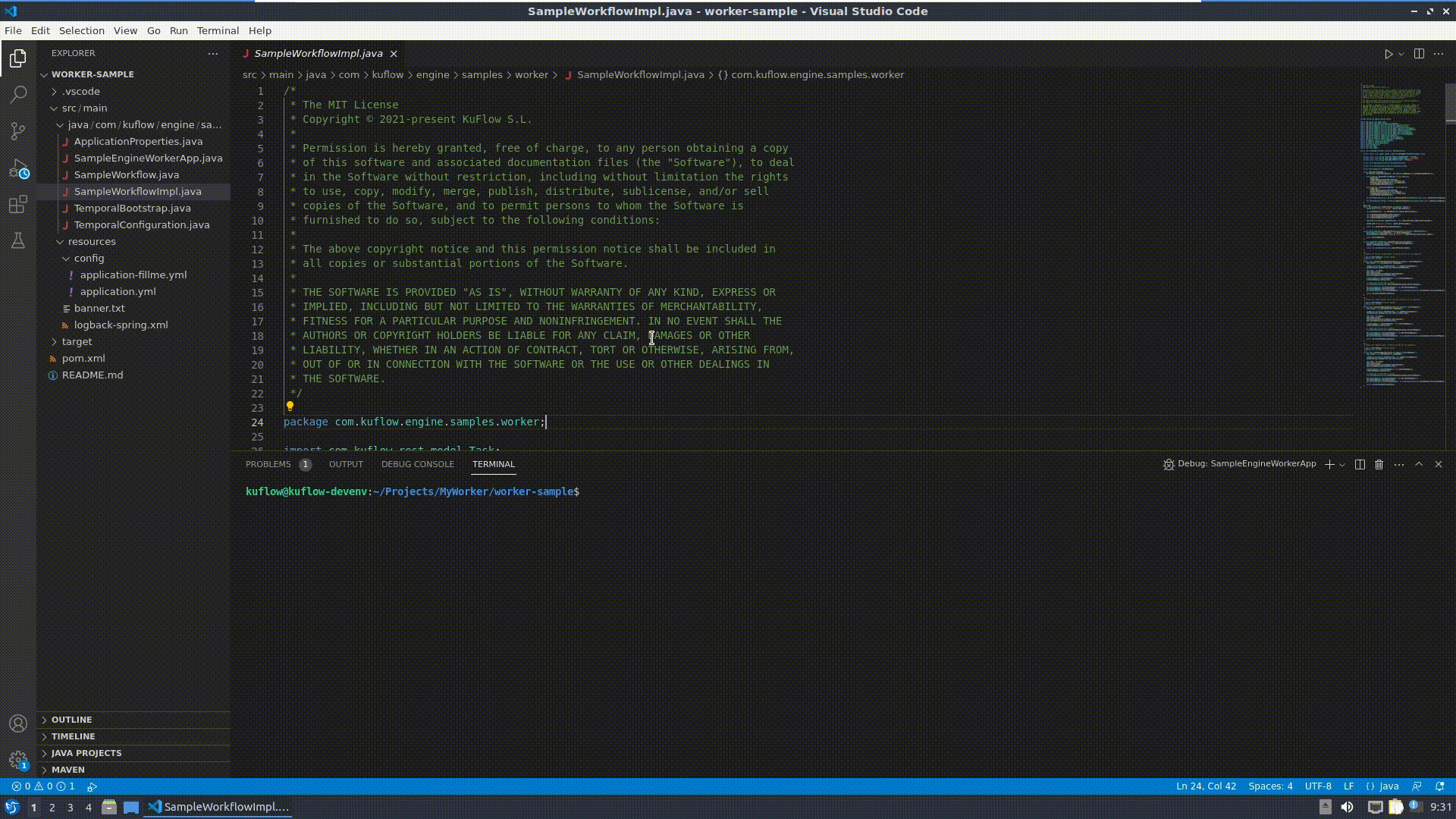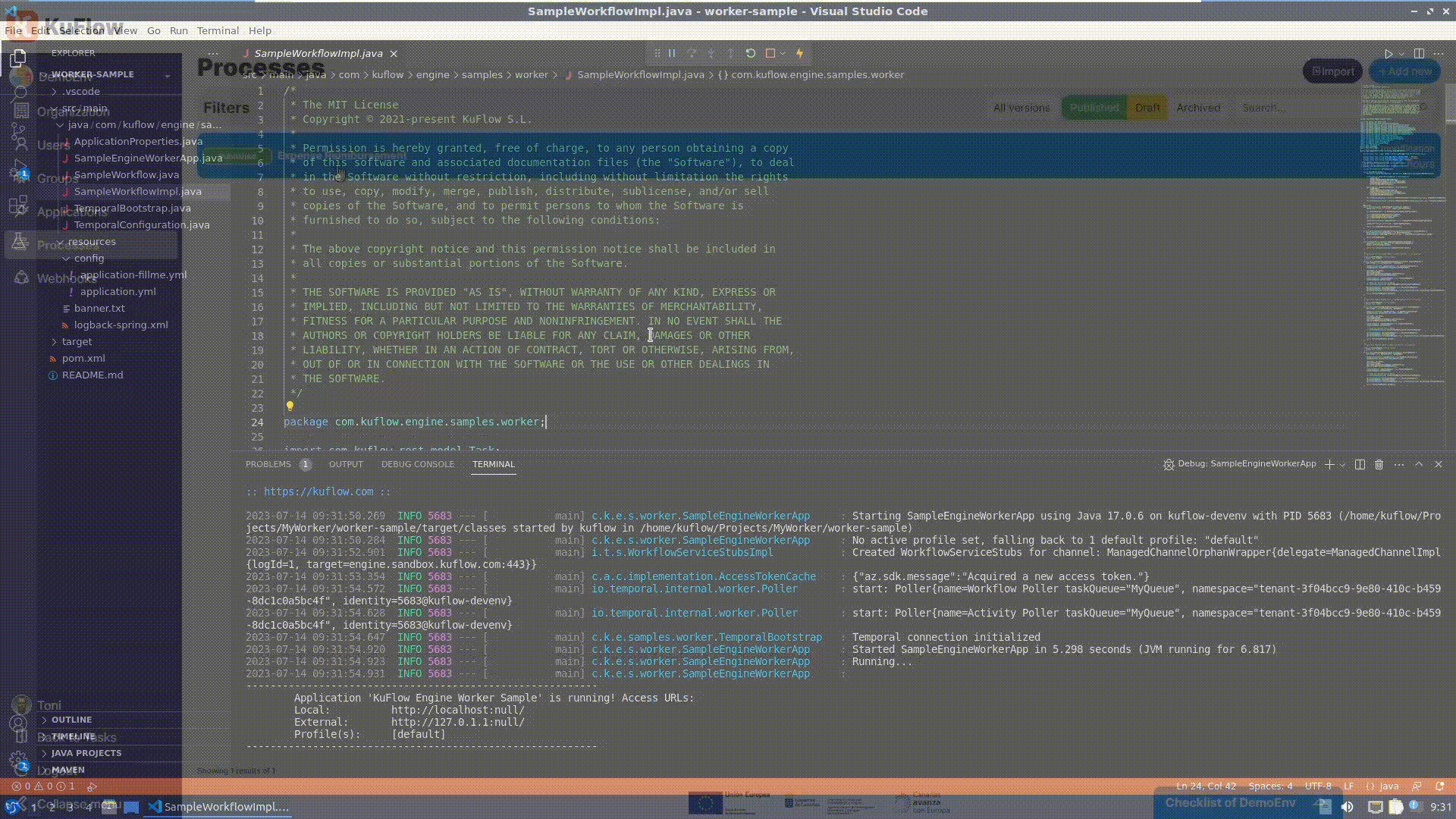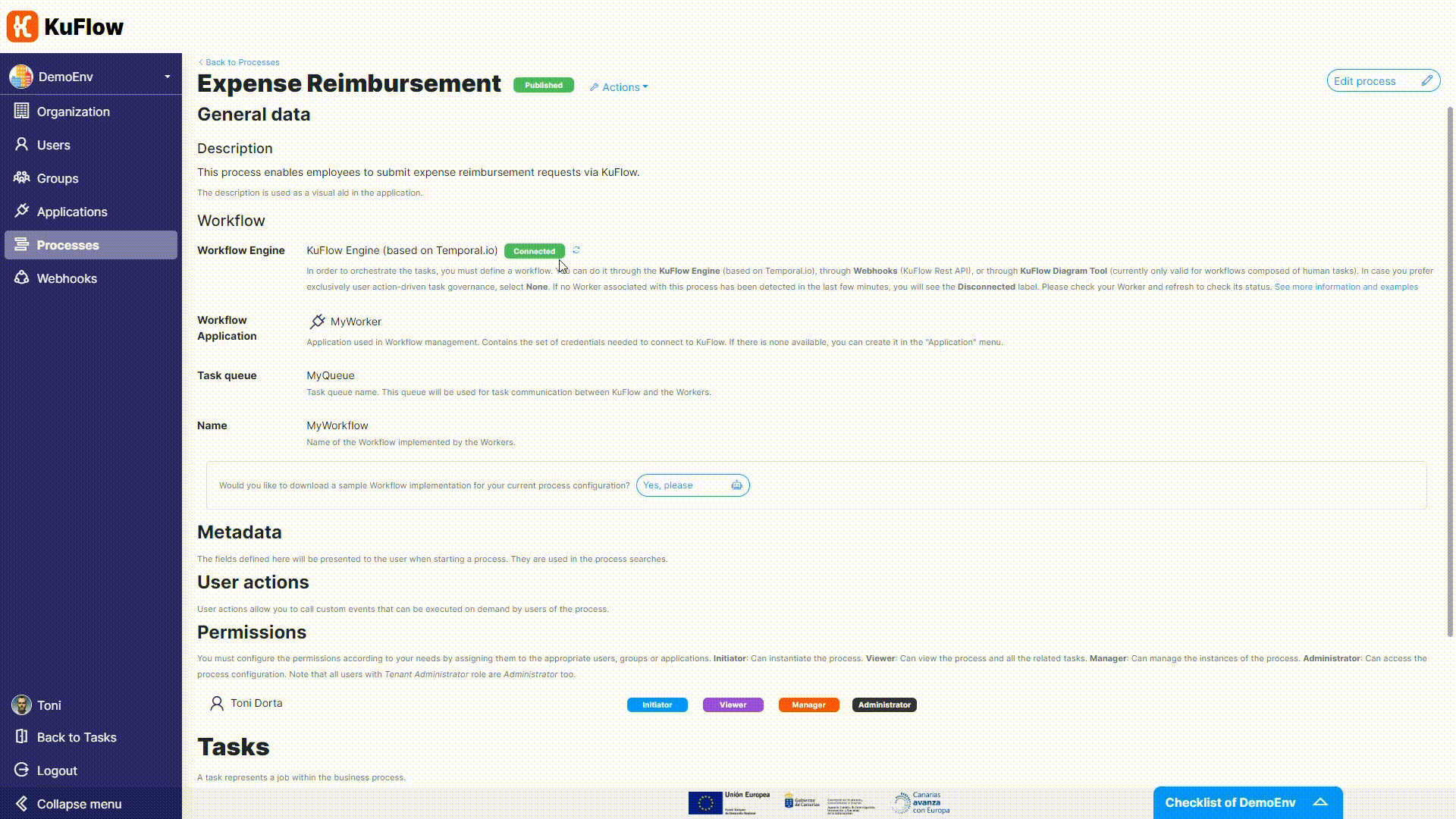
For the Process reimbursement task, we need to adjust permissions as we want that the worker will take charge of it.
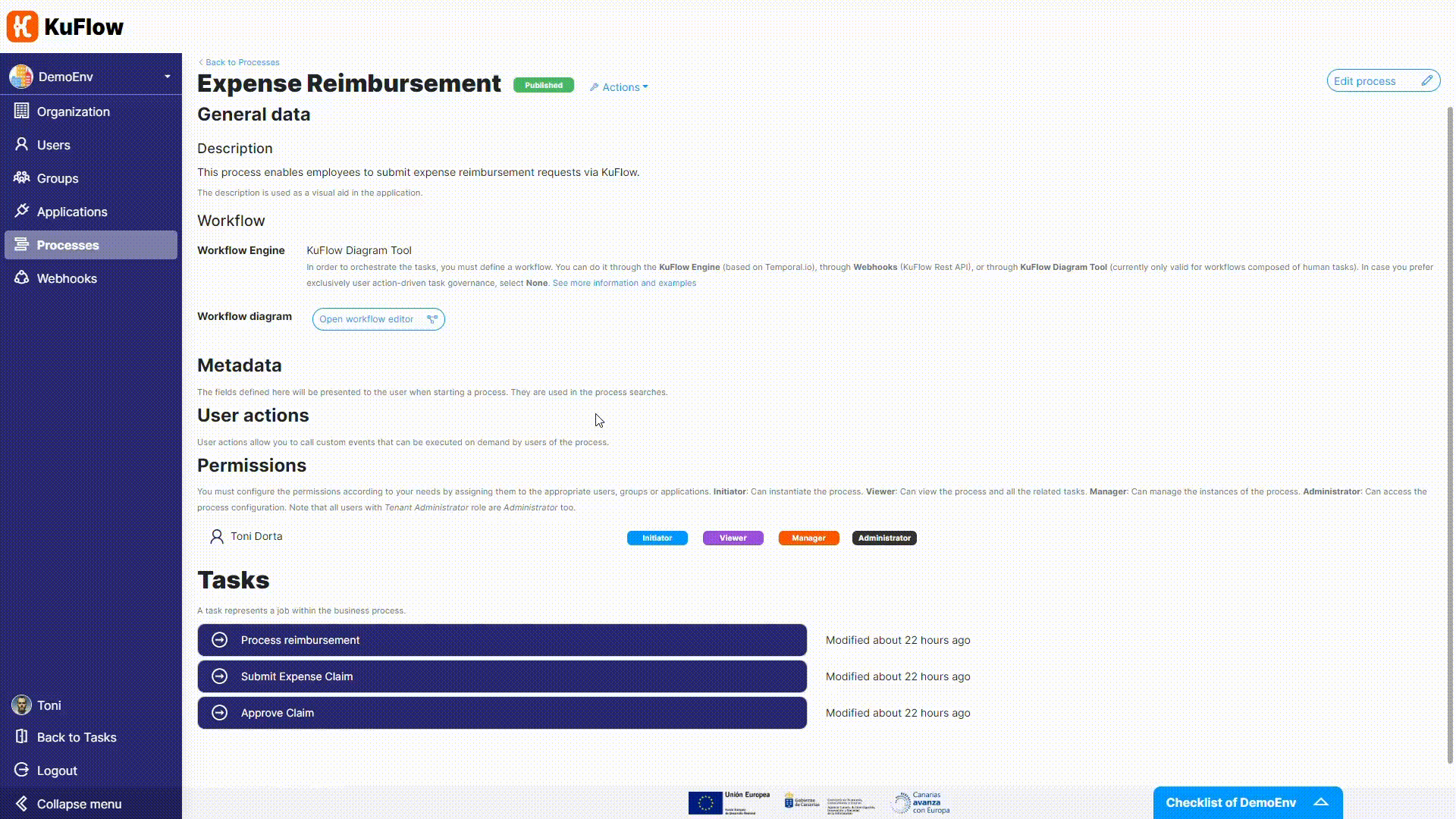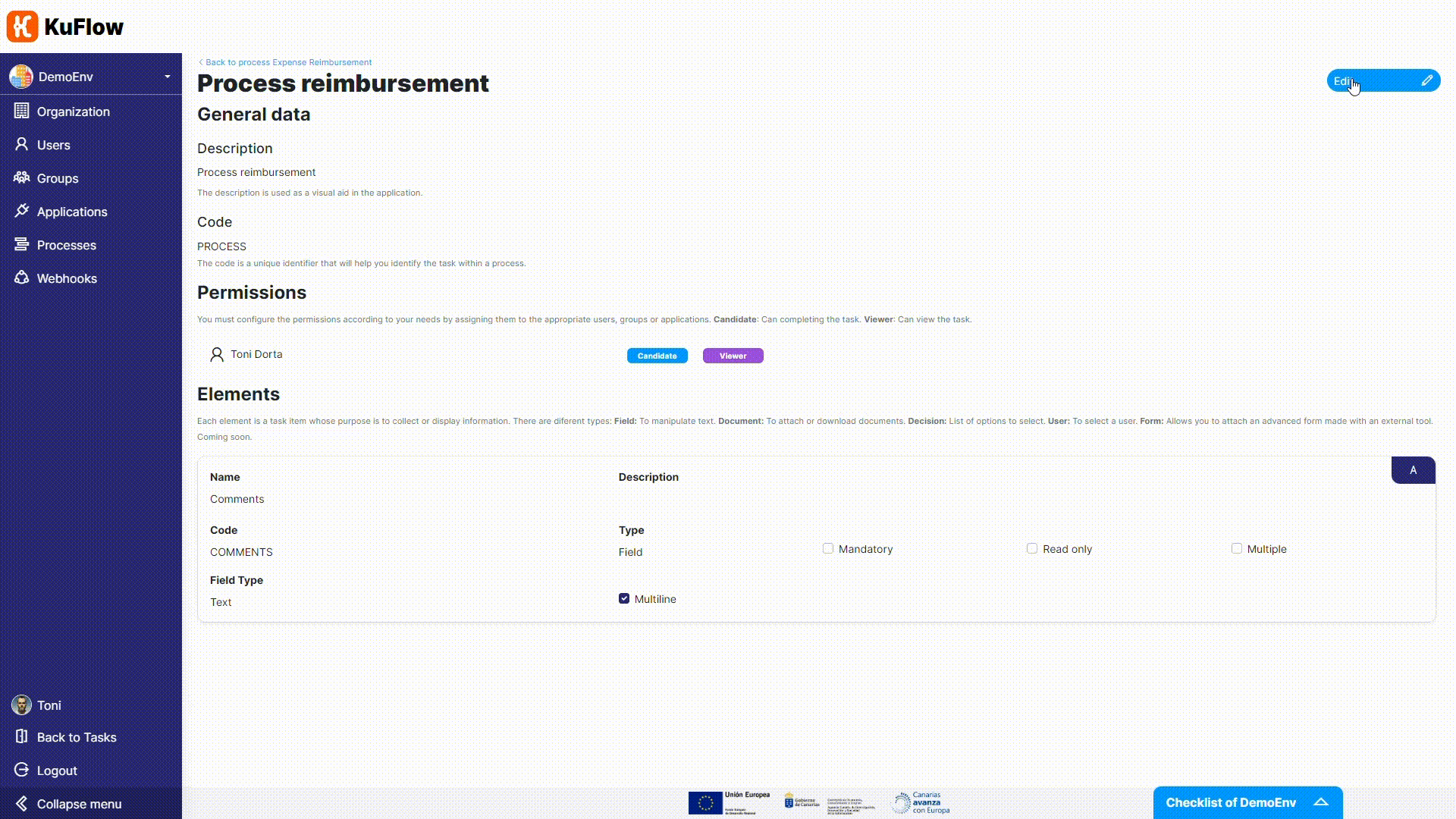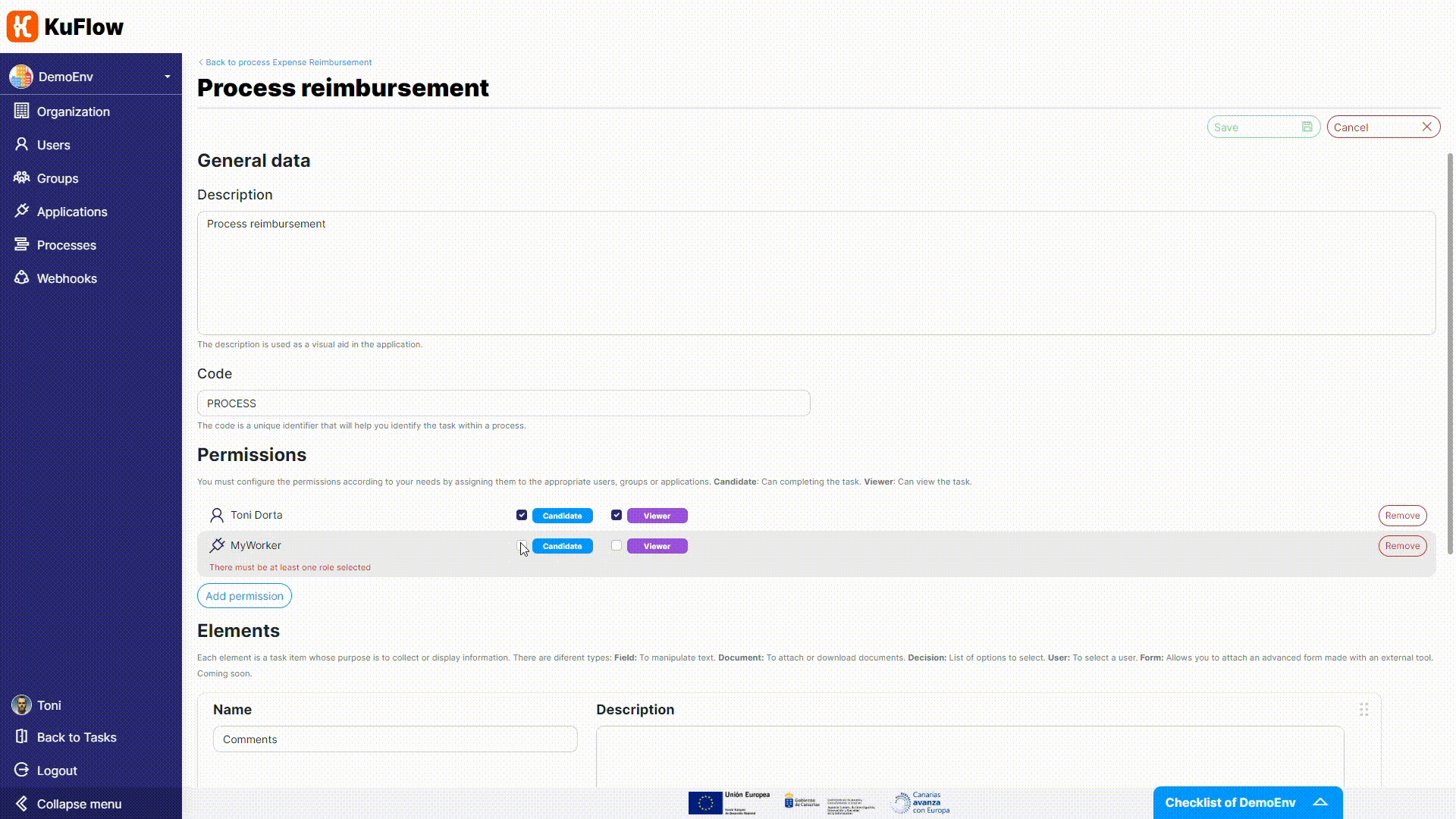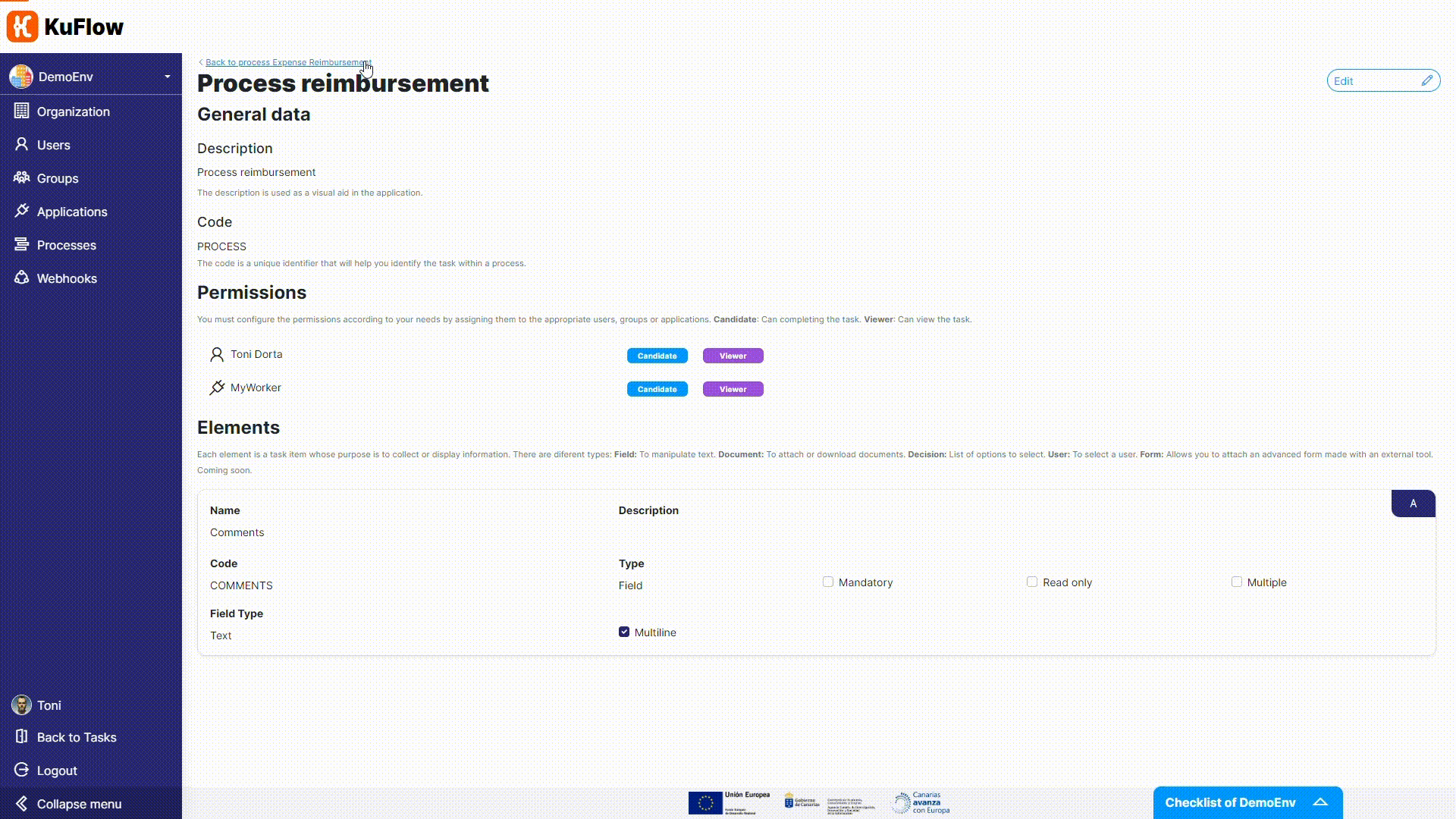
Now it is time to change the Workflow Engine. We are not longer using the Diagram Tool (technically, the Serverless Engine) but the based-on-Temporal KuFlow Engine.
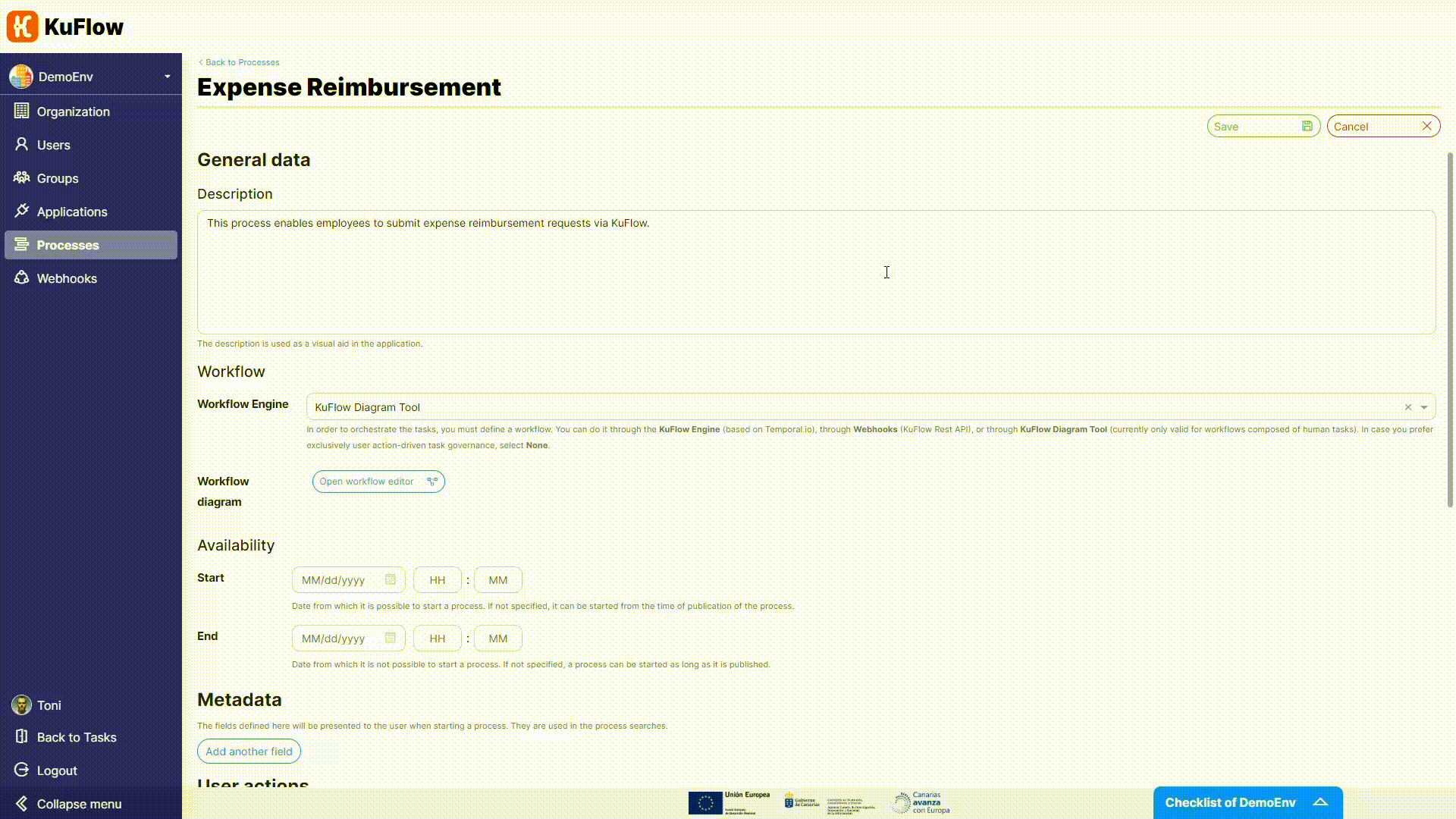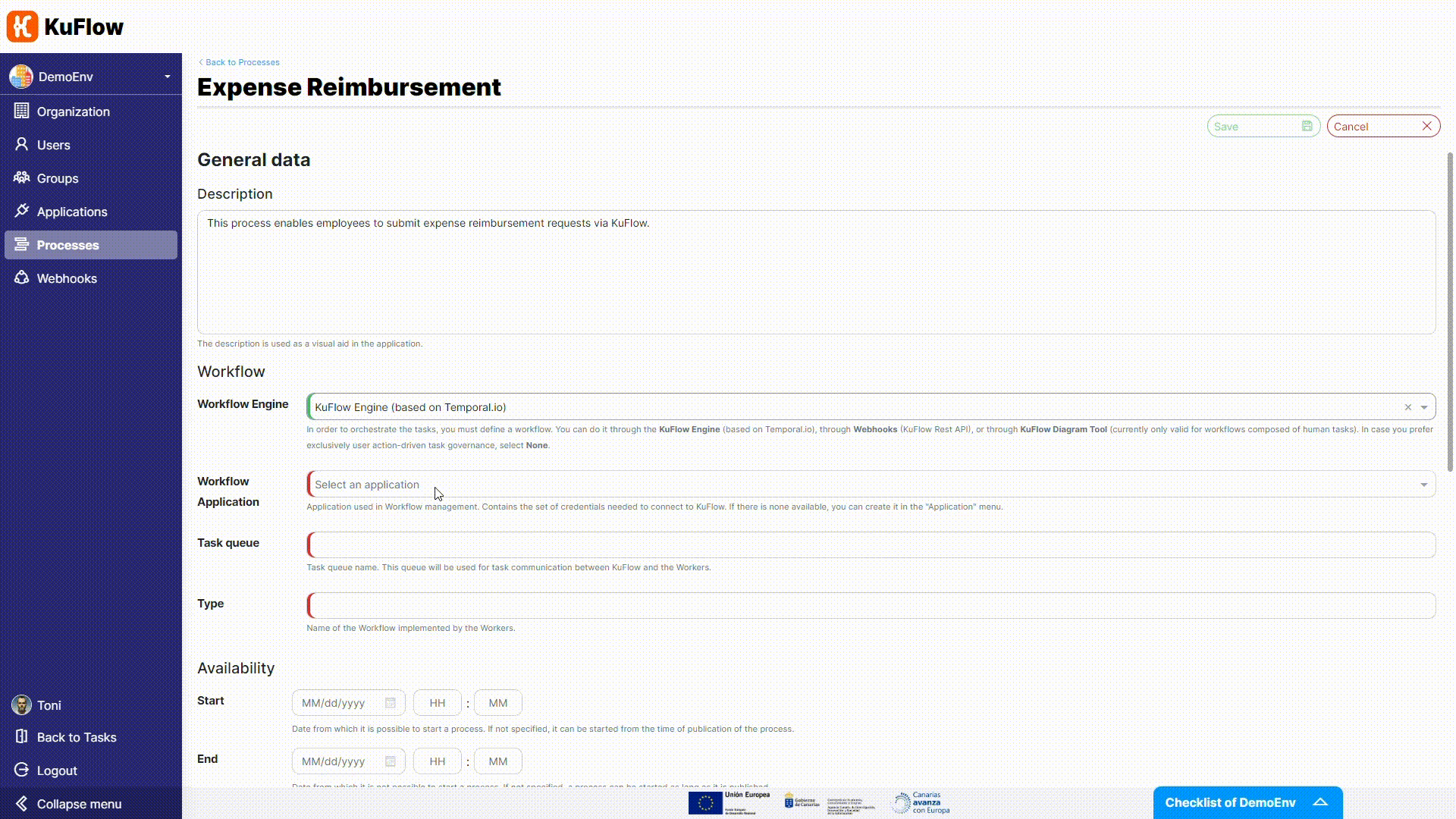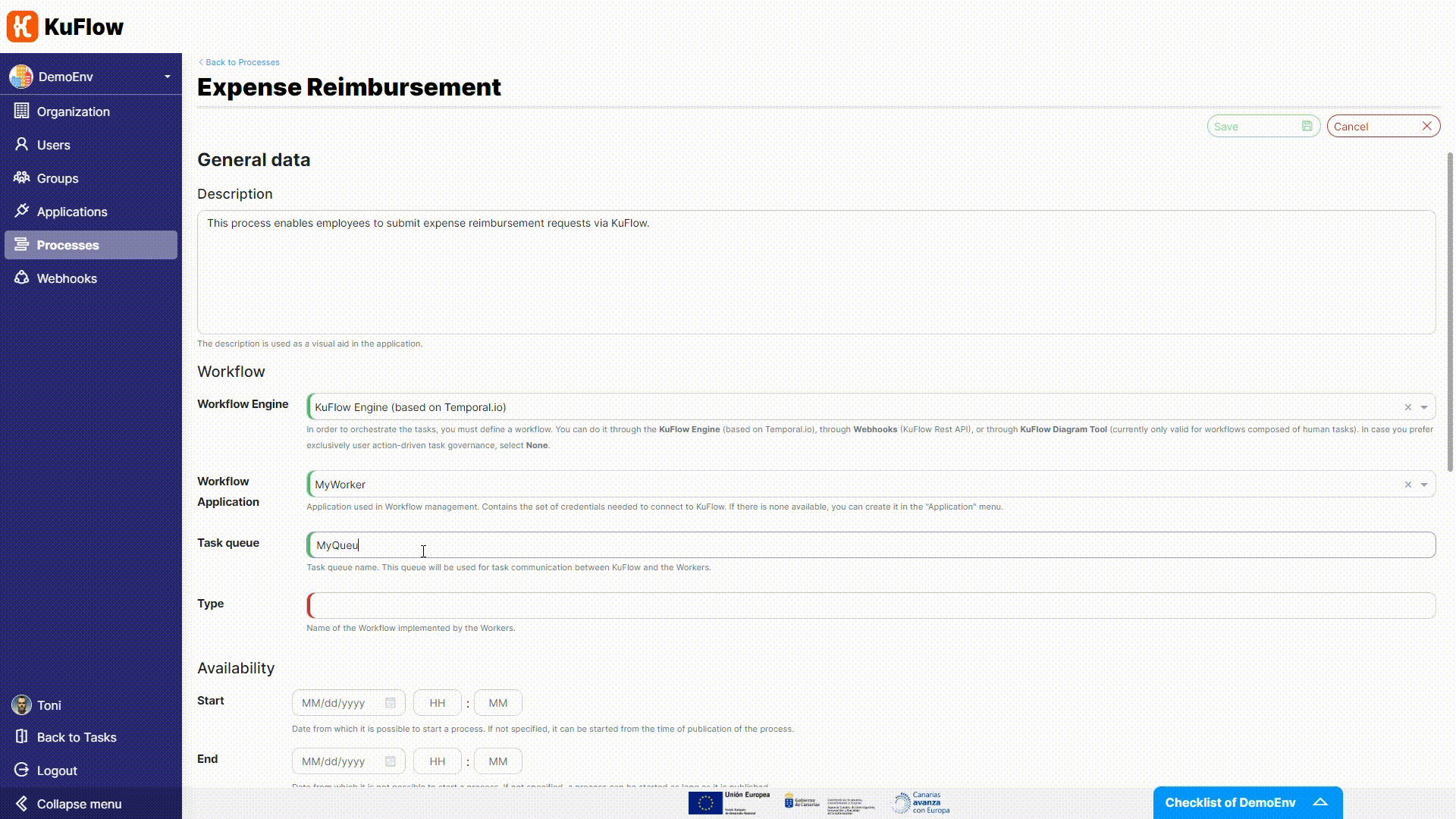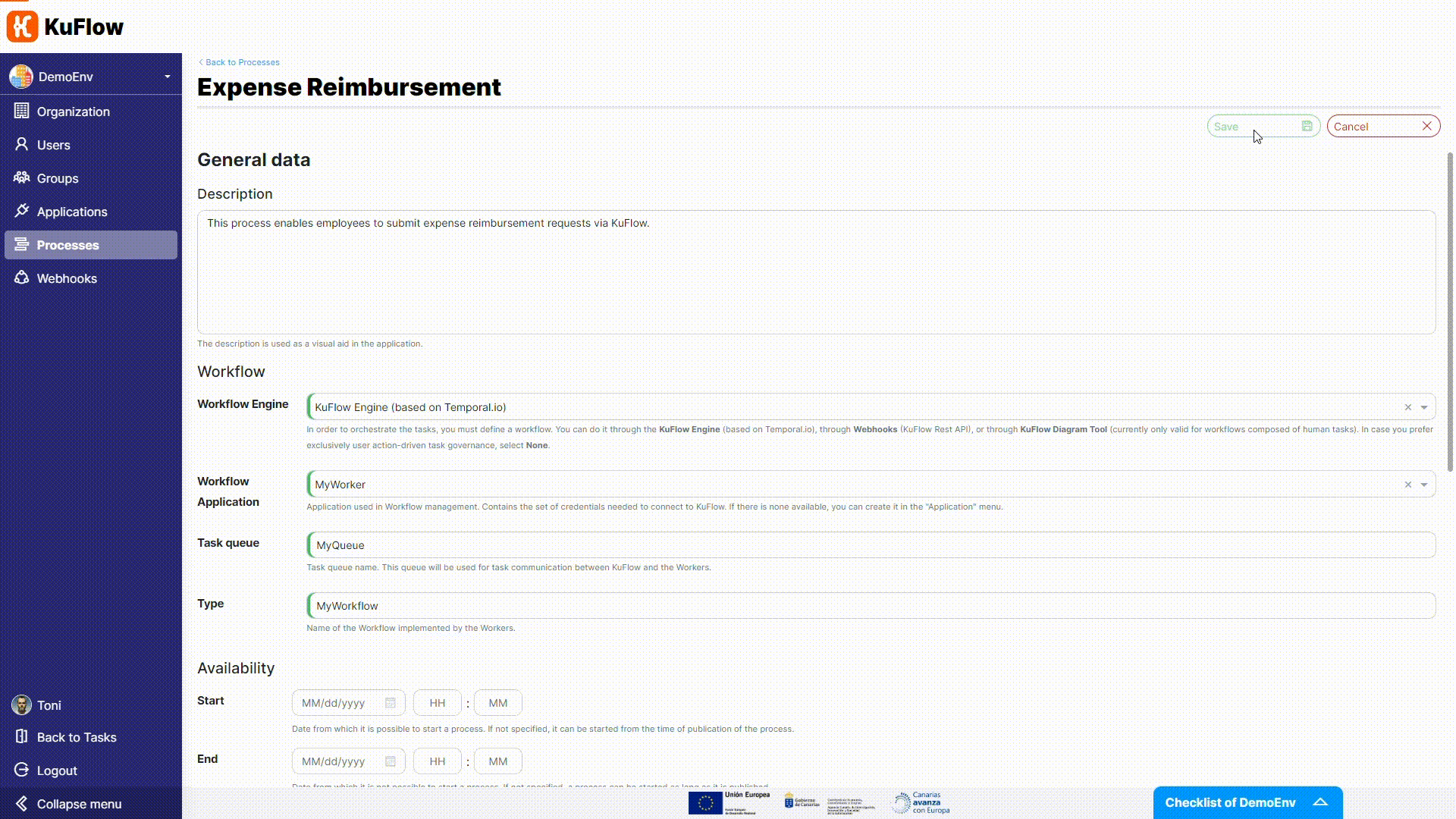
- Workflow application: MyWorker
- Task queue: MyQueue
- Type: MyWorkflow
Once we have made the adjustments in the process definition, it is time to work on the worker (forgive the redundancy).
We can save a lot of coding time asking KuFlow to provide us with a sample implementation for any process definition. In this case we are choosing Java as the implementation language (other languages to be added to this tutorial soon).

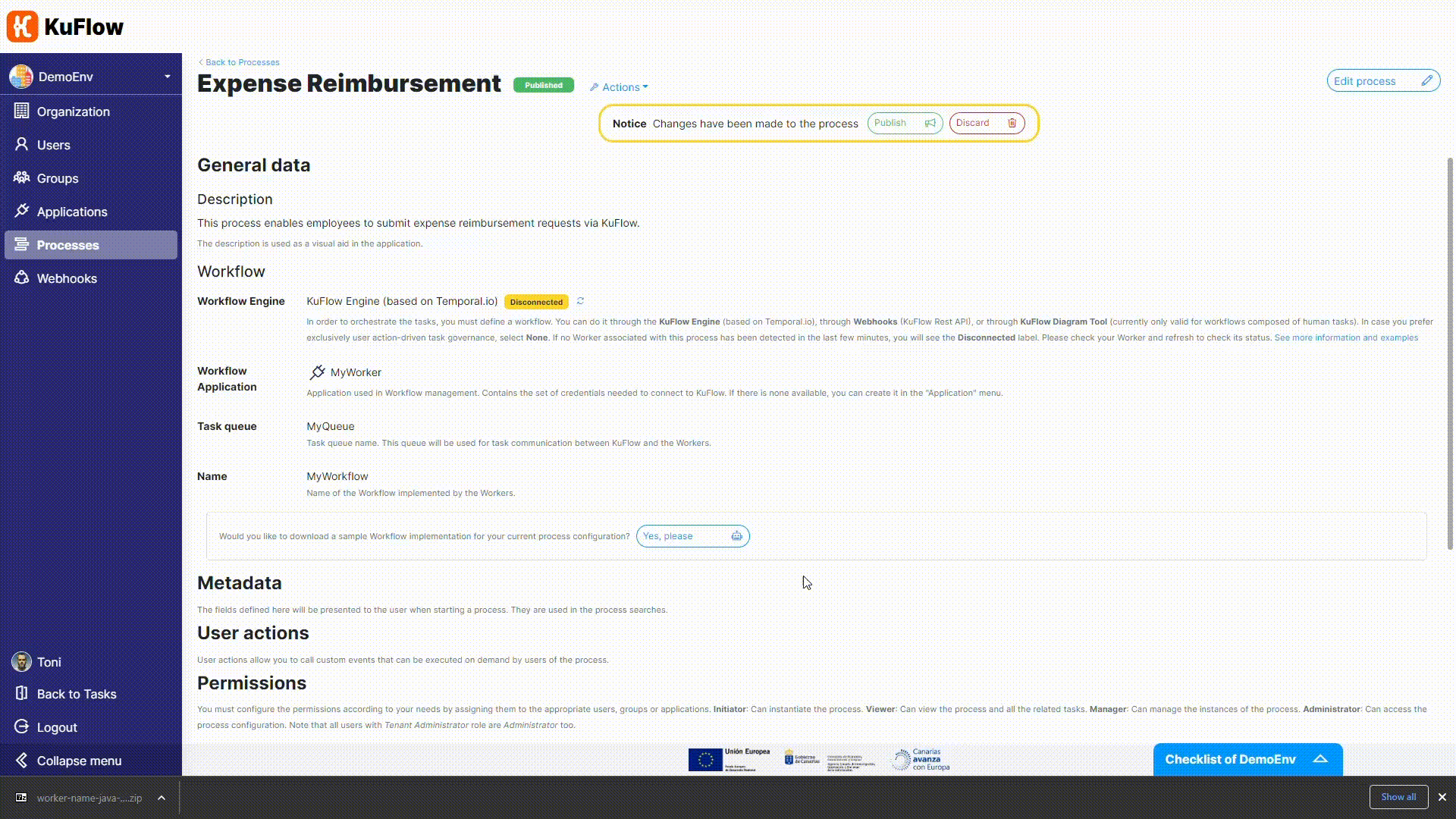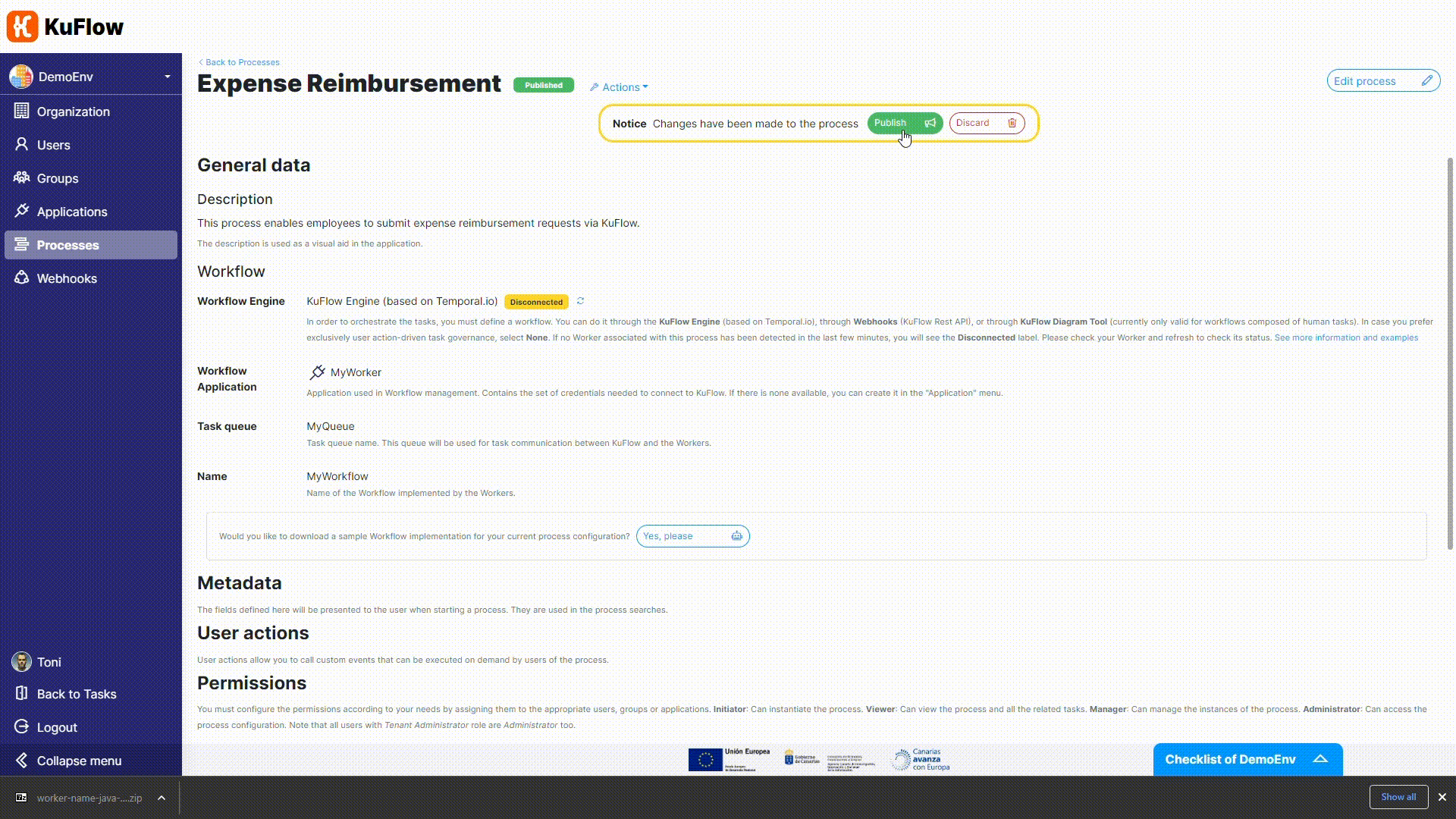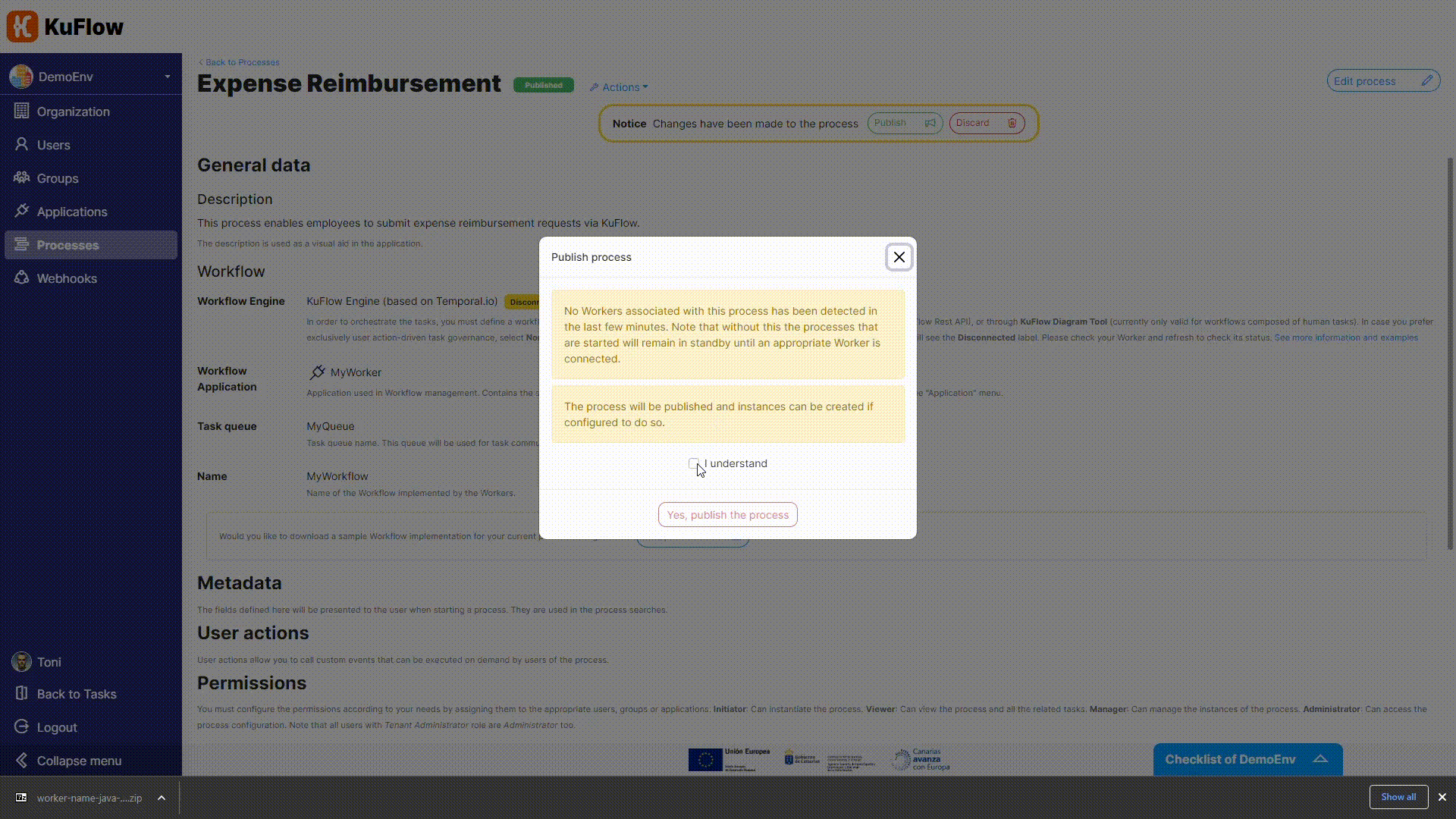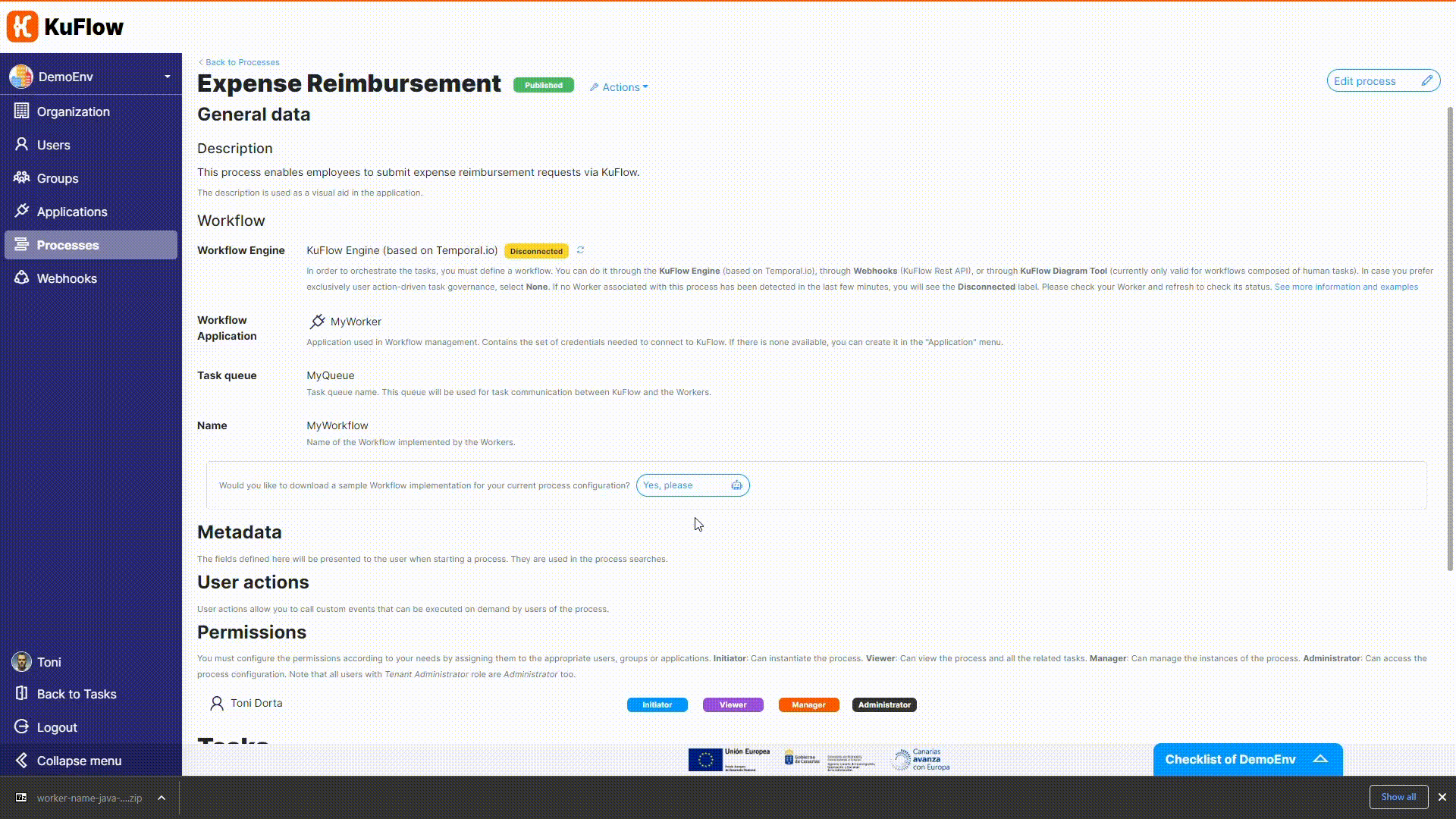
Now it is time to publish the process, as it doesn't require any additional changes.
One of the first things to do when preparing a KuFlow worker is to make the arrangements for establishing a connection with the cloud platform.
Modify the application-fillme.yml file, specifying the information of the token and the certificate keys.
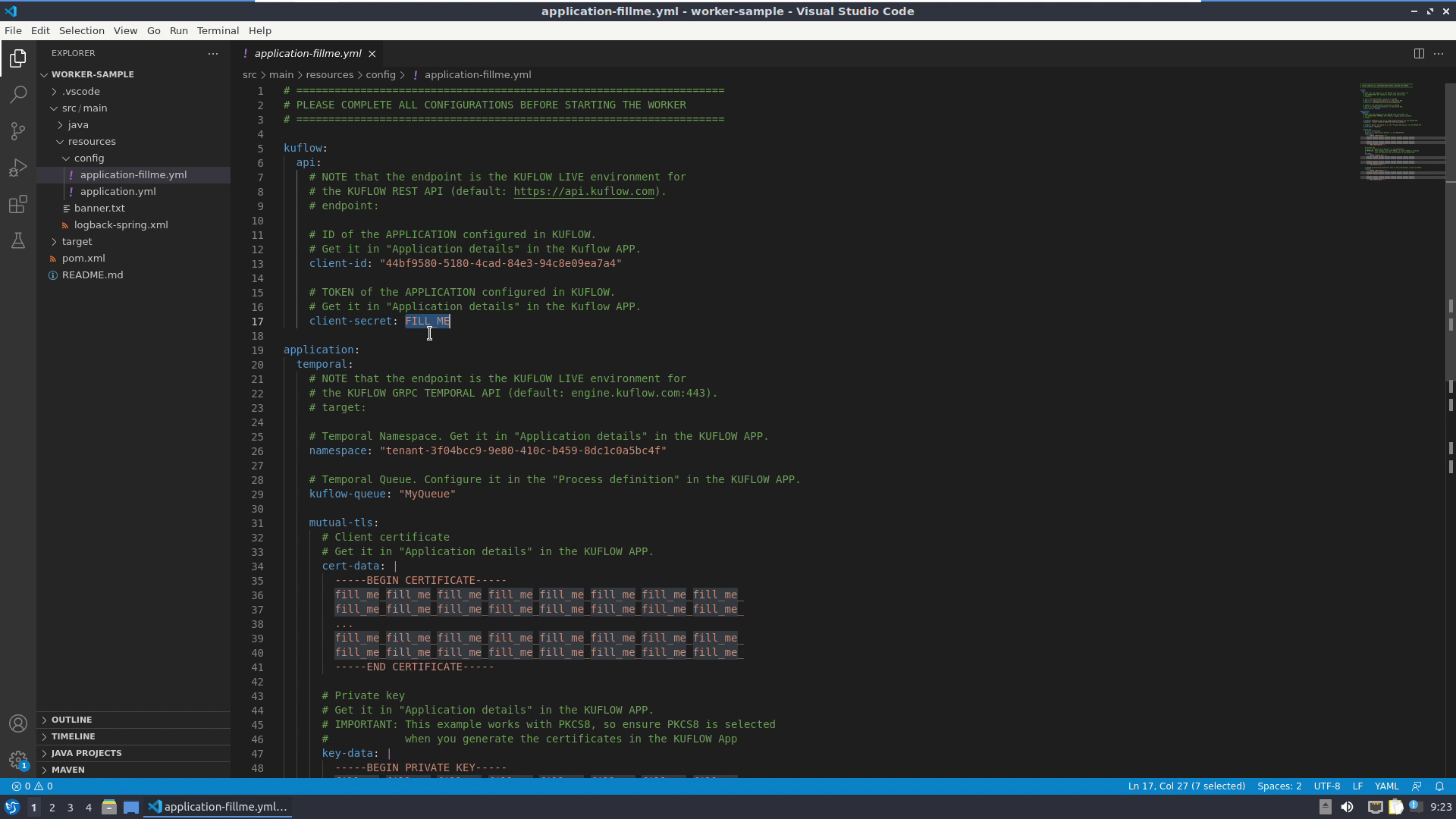
After specifying the connection parameters, run the Java project and check that the connection of the worker is well established.
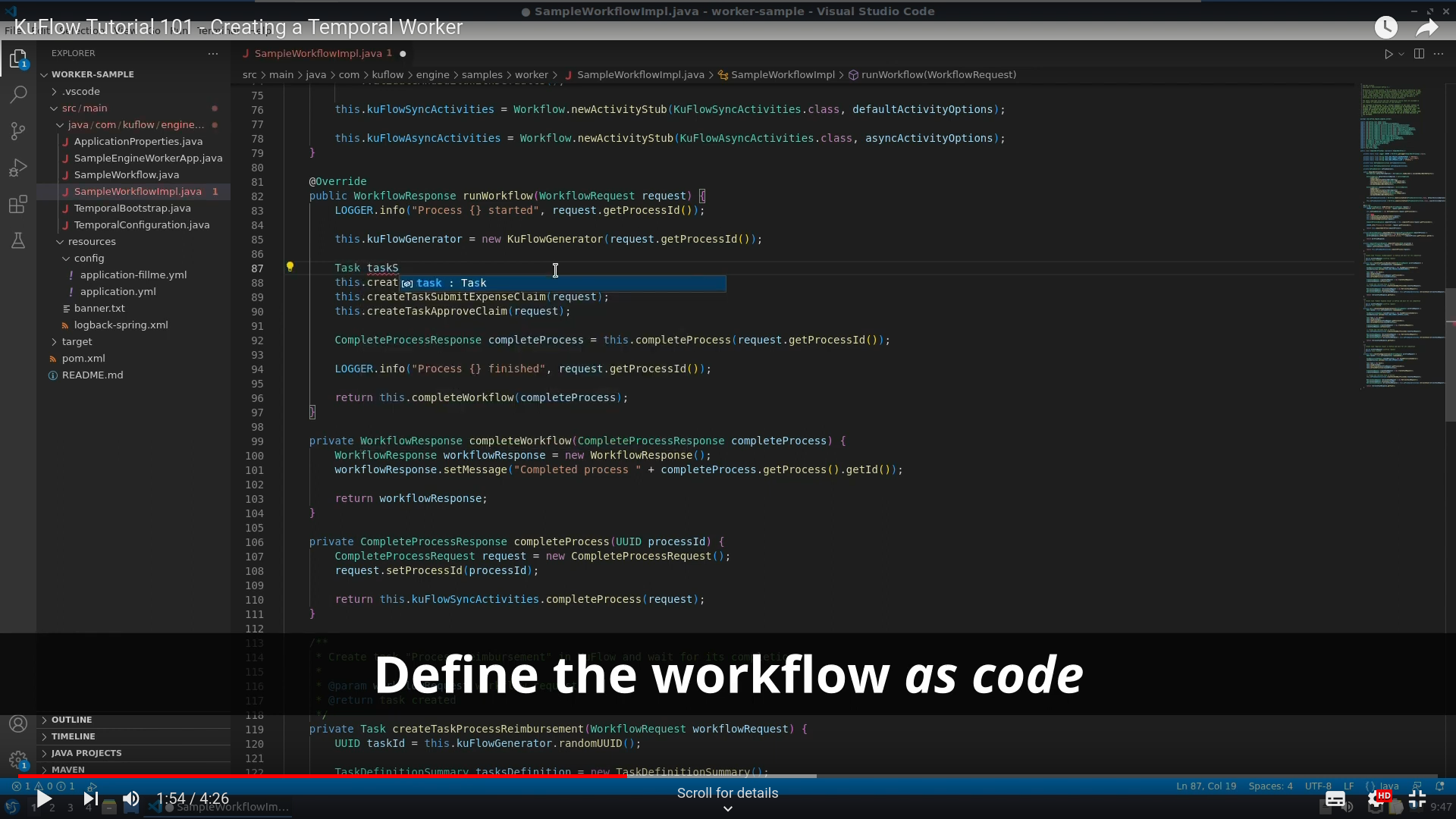
Now it is time to modify the worker, editing SampleWorkflowImpl.java:
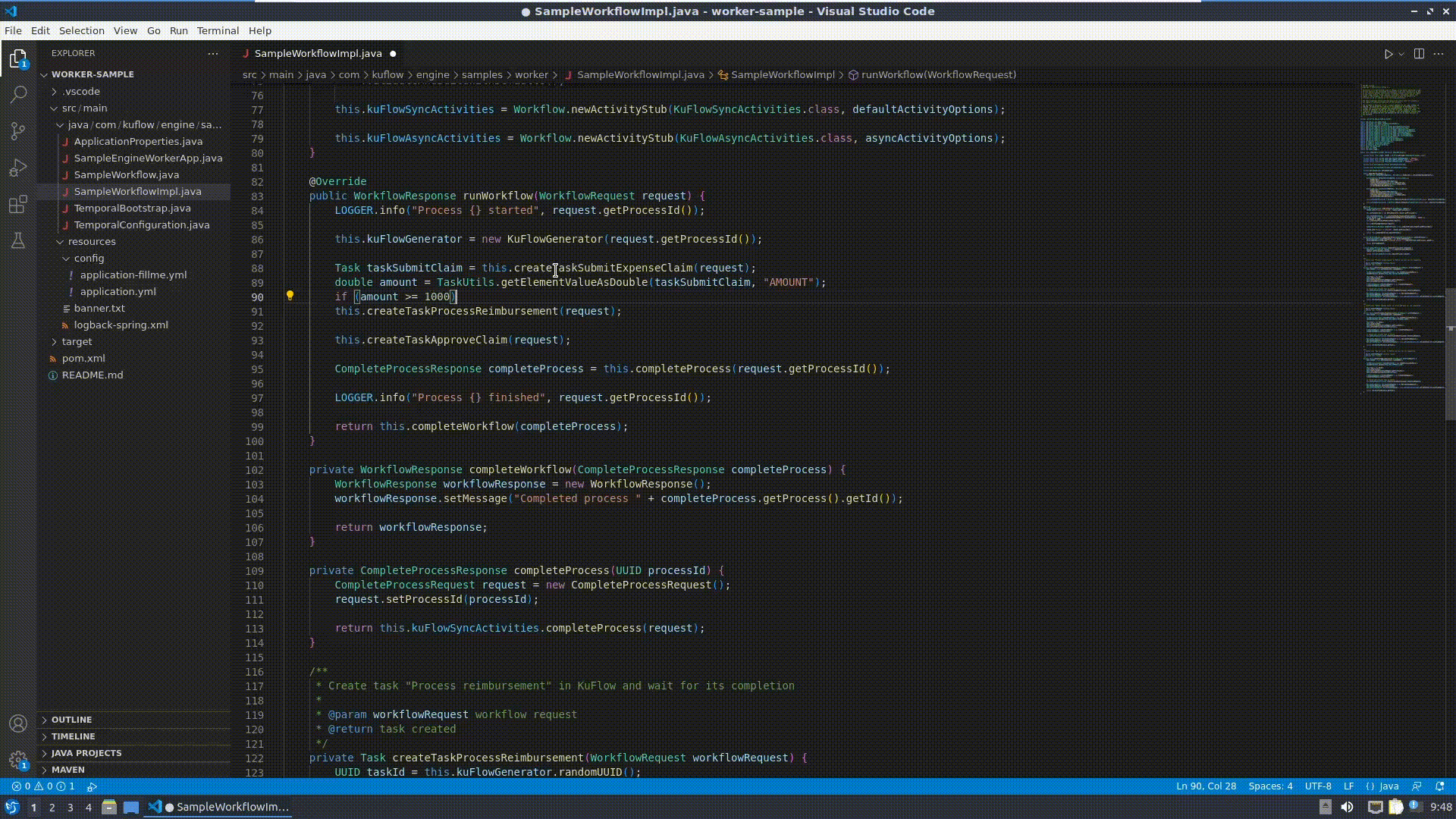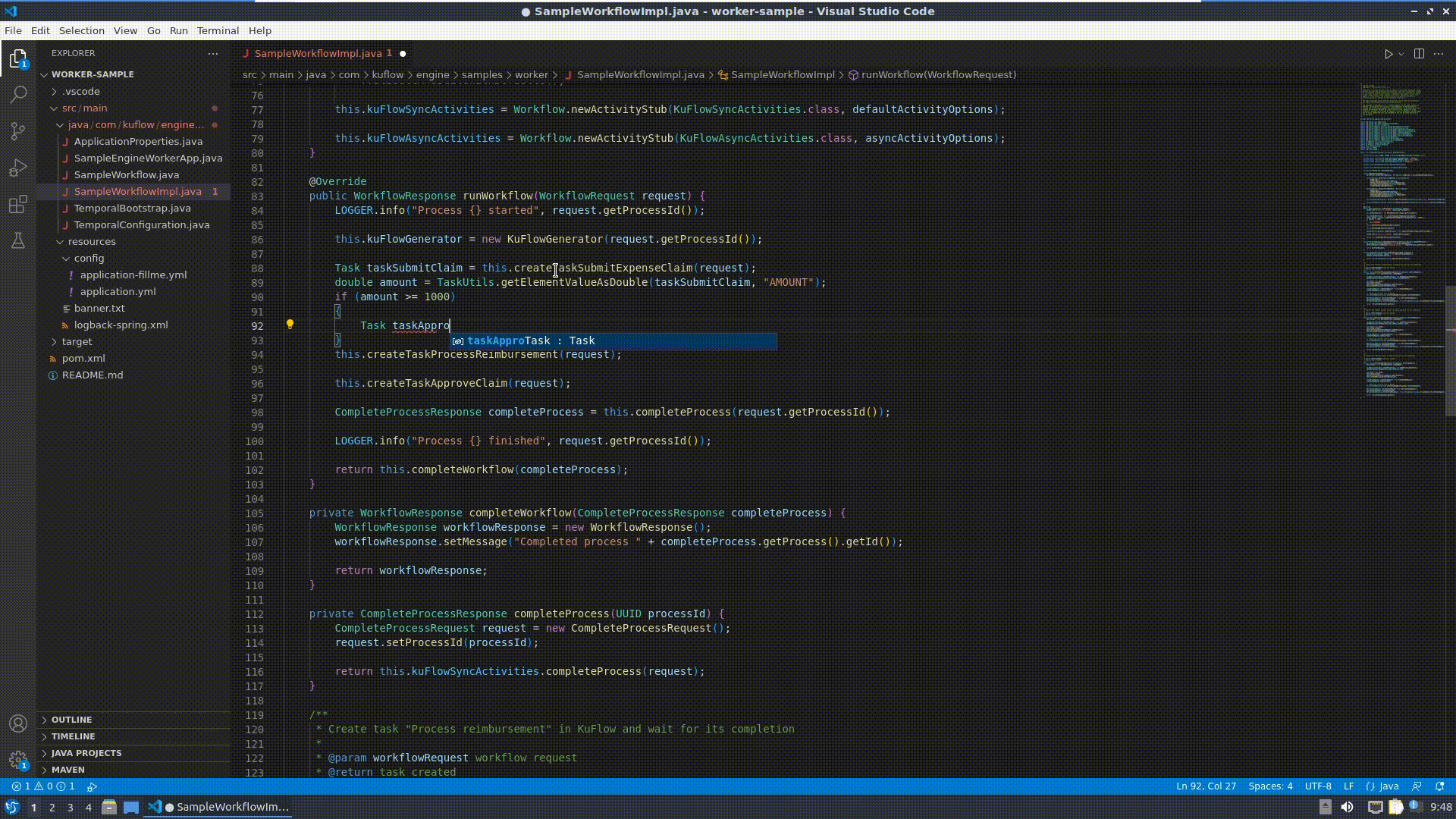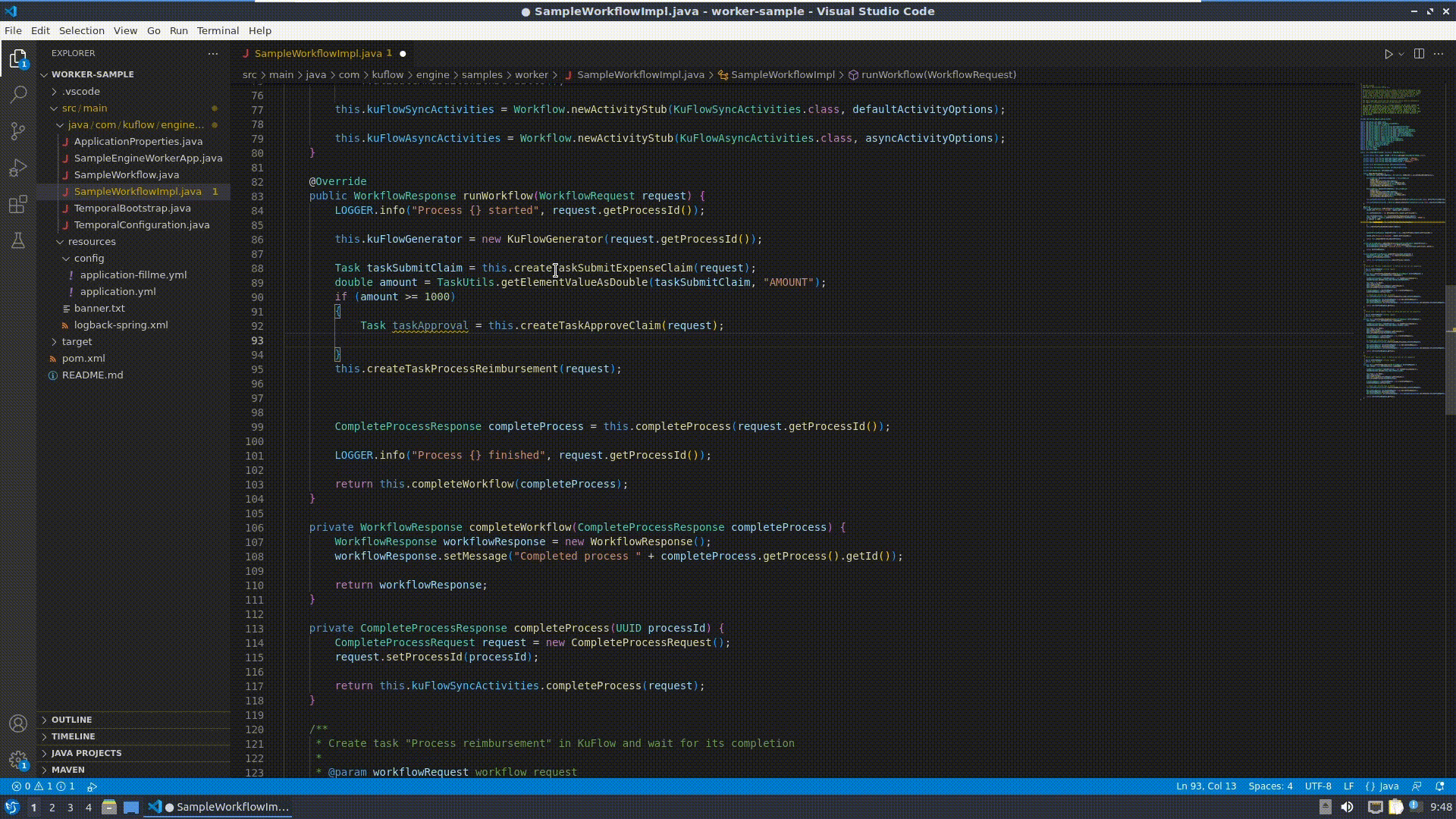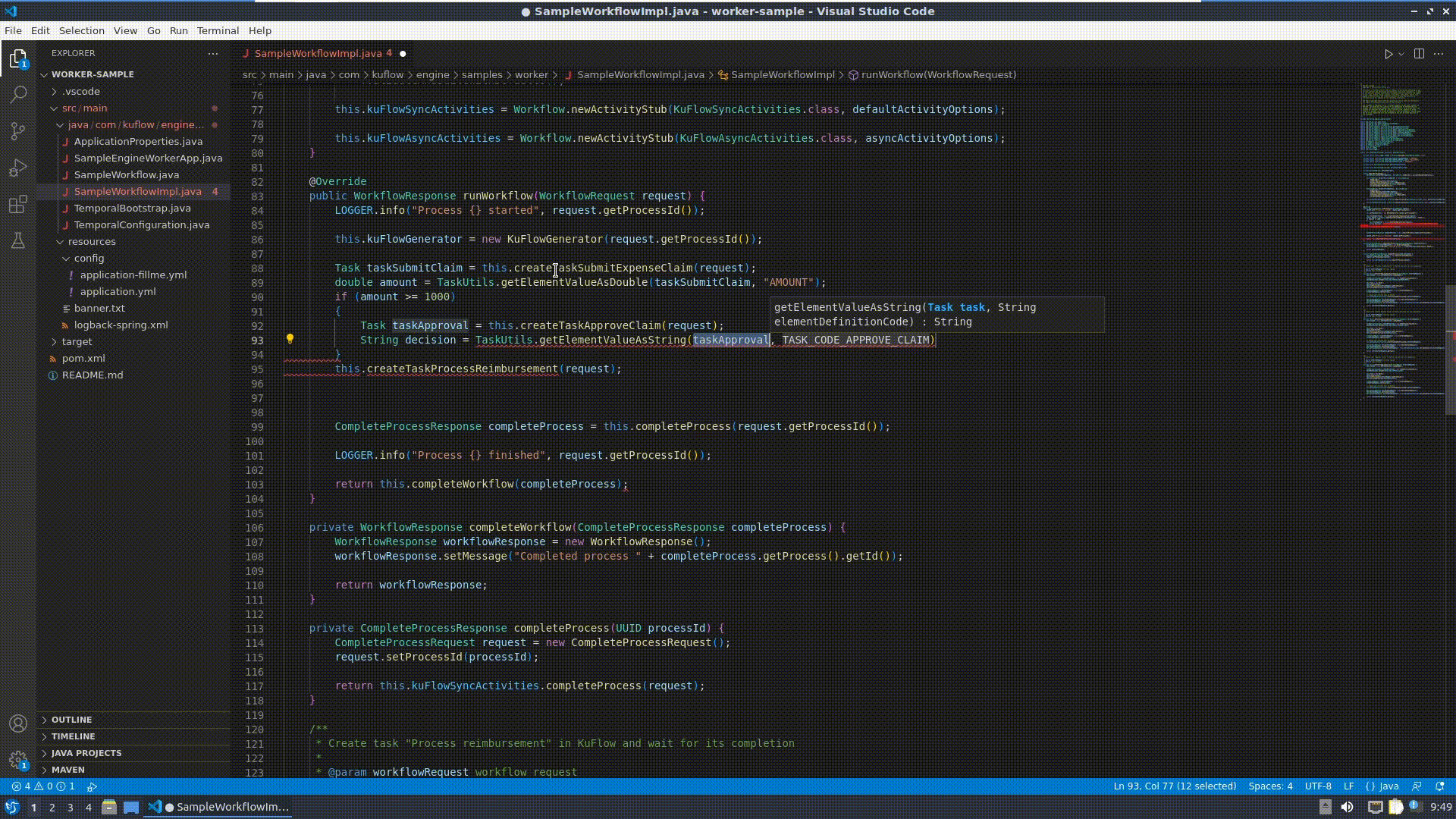
Change the runWorkflow() method:
@Override
public WorkflowResponse runWorkflow(WorkflowRequest request) {
LOGGER.info("Process {} started", request.getProcessId());
// --- New code ---
ProcessItem processItemSubmitClaim = this.createProcessItemSubmitExpenseClaim(request);
String amount = processItemkSubmitClaim.getTask().getData().getValue().get("AMOUNT").toString();
if (Double.valueOf(amount) >= 1_000) {
ProcessItem processItemApproval = this.createProcessItemApproveClaim(request);
String decision = processItemApproval.getTask().getData().getValue().get("DECISION").toString());
if (decision.equals("Y")) {
this.createProcessItemProcessReimbursement(request);
}
} else {
this.createProcessItemProcessReimbursement(request);
}
// ---------
LOGGER.info("Process {} finished", request.getProcessId());
return this.completeWorkflow(completeProcess);
}
And modify createProcessItemProcessReimbursement():
/**
* Create process item "Process reimbursement" in KuFlow and wait for its completion
*
* @param workflowRequest workflow request
* @return task created
*/
private Task createProcessItemProcessReimbursement(WorkflowRequest workflowRequest) {
UUID processItemId = KuFlowWorkflow.generateUUIDv7();
JsonValue createTaskData = new JsonValue();
createTaskData.setValue(Map.of("COMMENTS", "Processed automatically");
ProcessItemTaskCreateParams createTaskRequest = new ProcessItemTaskCreateParams();
createTaskRequest.setTaskDefinitionCode(TASK_CODE_PROCESS_REIMBURSEMENT);
createTaskRequest.setData(createTaskData);
TaskDefinitionSummary tasksDefinition = new TaskDefinitionSummary();
tasksDefinition.setCode(TASK_CODE_PROCESS_REIMBURSEMENT);
ProcessItemCreateRequest createRequest = new ProcessItemCreateRequest();
createRequest.setId(processItemId);
createRequest.setType(ProcessItemType.TASK);
createRequest.setProcessId(workflowRequest.getProcessId());
createRequest.setTask(createTaskRequest);
// Create process item
this.kuFlowActivities.createProcessItem(createRequest);
// Wait for its external completion (outside this workflow, usually in the KuFlow APP or via Rest Api)
// This line is useful if you are orchestrating asynchronous tasks, e.g. those performed by humans.
// In the case of synchronous tasks, i.e. tasks that are completed by this Workflow itself,
// you should remove this line and do not forget to add code to complete the task programmatically.
Workflow.await(() -> this.kuFlowCompletedTaskIds.contains(processItemId));
// Claim task
ProcessItemTaskClaimRequest claimRequest = new ProcessItemTaskClaimRequest();
claimRequest.setProcessItemId(processItemId);
this.kuFlowSyncActivities.claimProcessItemTask(claimRequest);
// TO-DO: Process reimbursement in third party systems (or whatever)
// ...
// Complete task
ProcessItemTaskCompleteRequest completeRequest = new ProcessItemTaskCompleteRequest();
completeRequest.setProcessItemId(processItemId);
this.kuFlowSyncActivities.completeProcessItemTask(completeRequest);
// --- End of modifications
ProcessItemRetrieveRequest retrieveRequest = new ProcessItemRetrieveRequest();
retrieveRequest.setProcessItemId(processItemId);
ProcessItemRetrieveResponse retrieveResponse = this.kuFlowSyncActivities.retrieveProcessItem(retrieveTaskRequest);
return retrieveResponse.getProcessItem();
}
Finally, you can test the process definition starting some executions of this workflow. Please check as the workflow depends on the expense amount and on the decision of approval, and observe that the Process reimbursement task is now completed automatically (no user involvement needed).
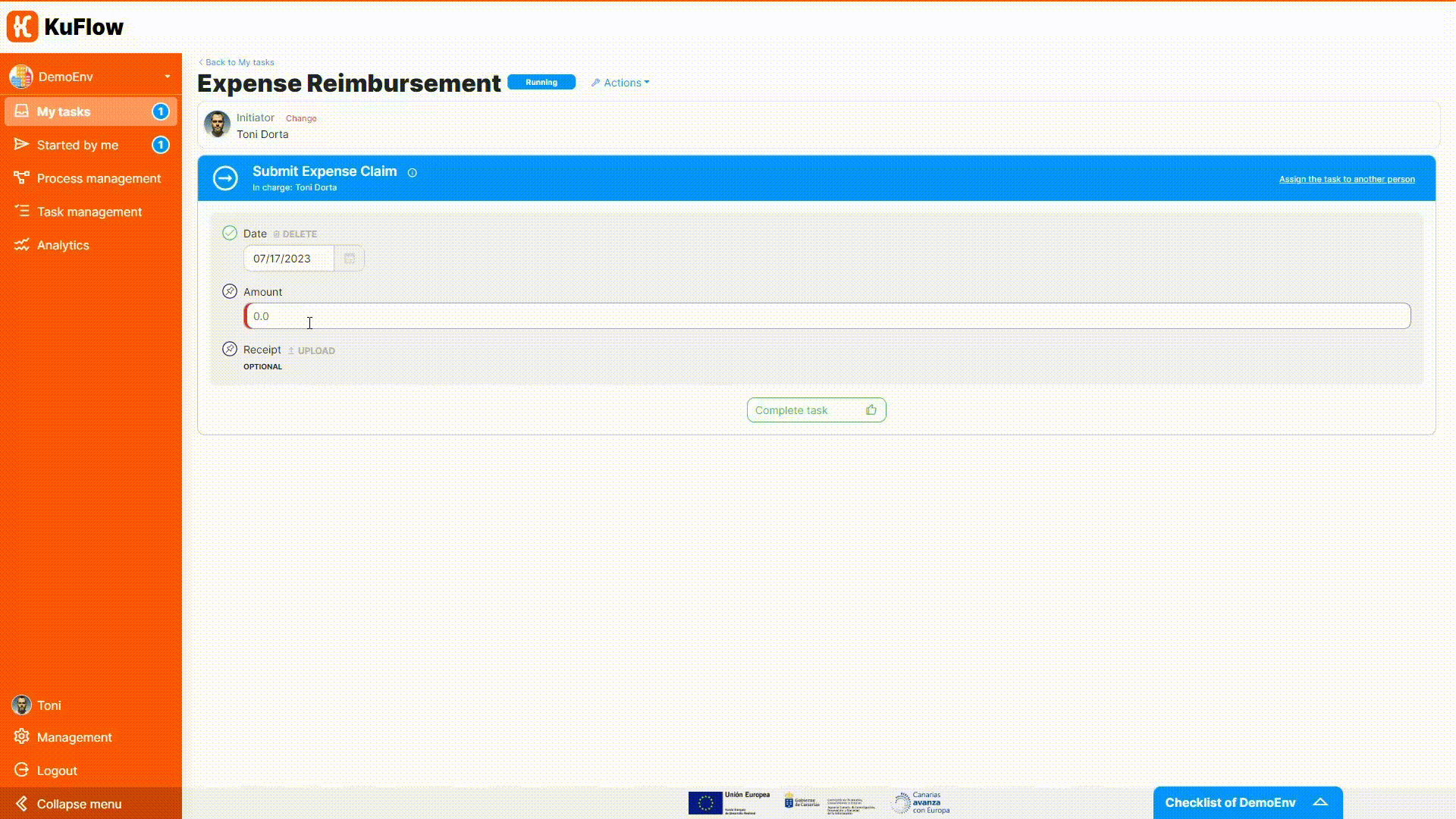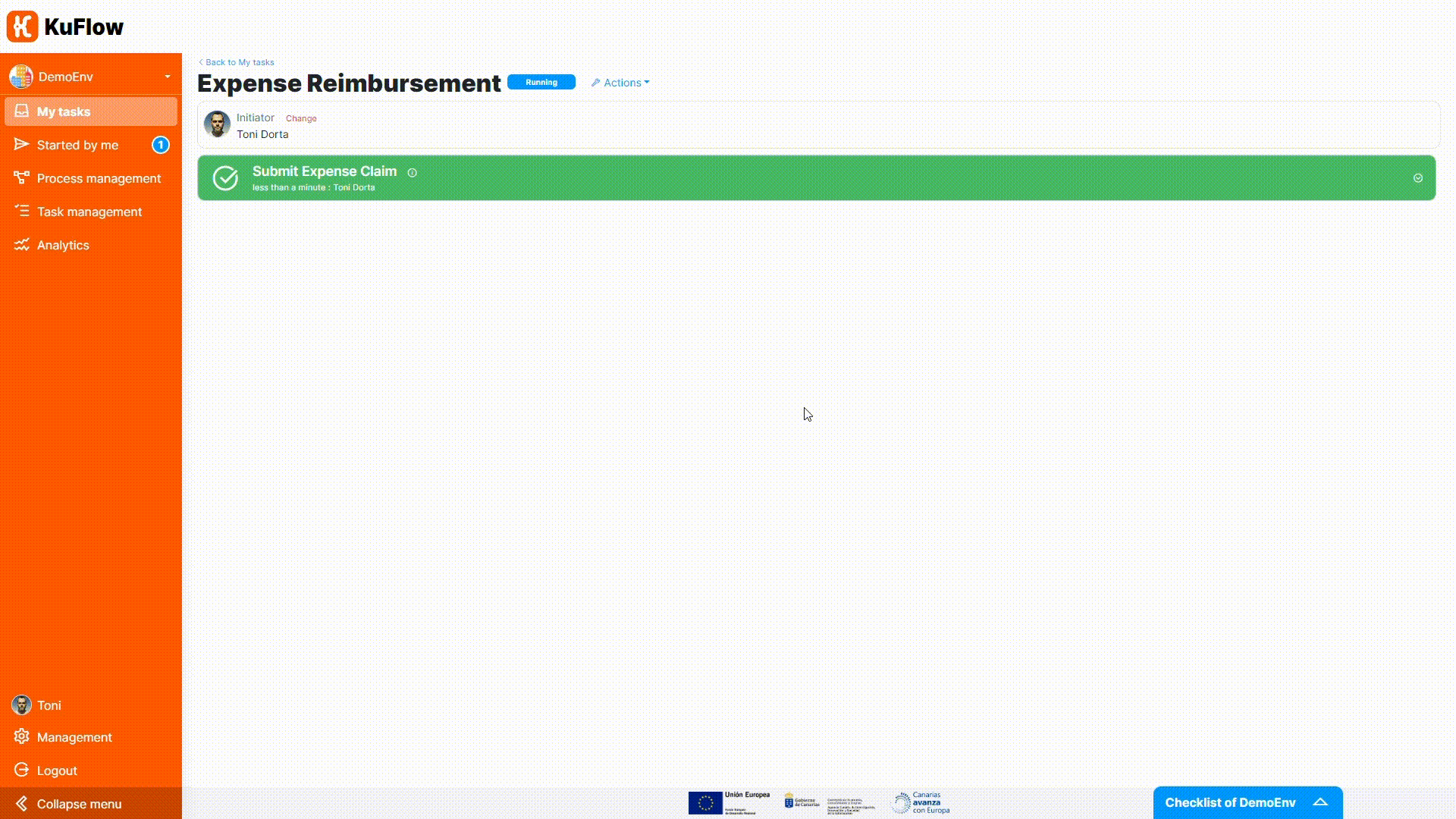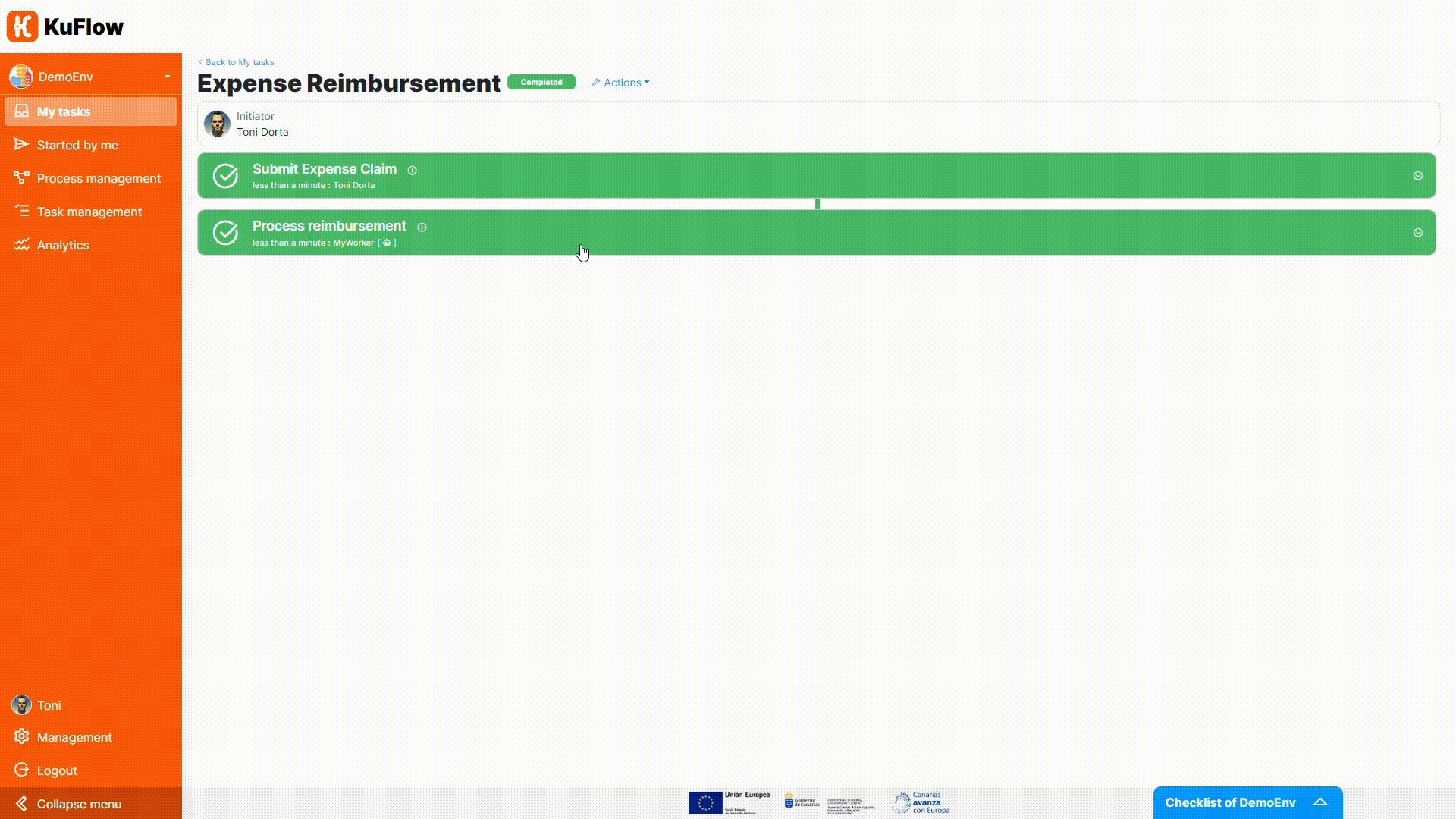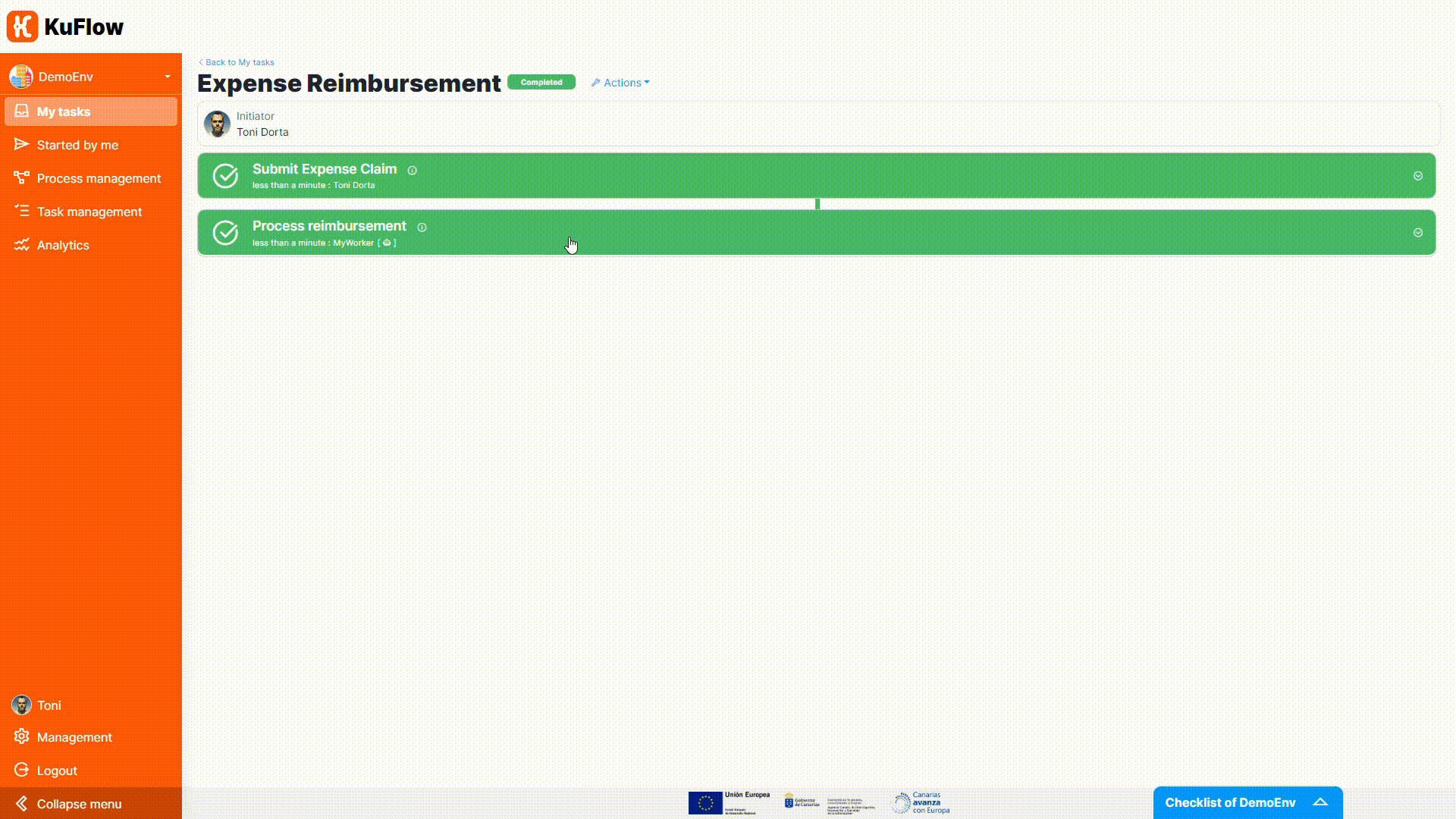
To help you tackle all the details of this step, we have prepared a small illustrative video that will guide you through the process of importing the template, downloading the Java project, adapting it to your needs, and executing the process.
We recommend that you follow the steps in the video carefully and experiment with the process once you've run it. This will be a big step forward in your understanding of KuFlow and will allow you to get the most out of the platform.
Don't miss the opportunity to tackle more complex processes on KuFlow and experience all that this platform has to offer!